Filter
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
public interface Filter {
/**
* Called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is being
* placed into service. The servlet container calls the init method exactly
* once after instantiating the filter. The init method must complete
* successfully before the filter is asked to do any filtering work.
* <p>
* The web container cannot place the filter into service if the init method
* either:
* <ul>
* <li>Throws a ServletException</li>
* <li>Does not return within a time period defined by the web
* container</li>
* </ul>
* The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*
* @param filterConfig The configuration information associated with the
* filter instance being initialised
*
* @throws ServletException if the initialisation fails
*/
public default void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
/**
* The <code>doFilter</code> method of the Filter is called by the container
* each time a request/response pair is passed through the chain due to a
* client request for a resource at the end of the chain. The FilterChain
* passed in to this method allows the Filter to pass on the request and
* response to the next entity in the chain.
* <p>
* A typical implementation of this method would follow the following
* pattern:- <br>
* 1. Examine the request<br>
* 2. Optionally wrap the request object with a custom implementation to
* filter content or headers for input filtering <br>
* 3. Optionally wrap the response object with a custom implementation to
* filter content or headers for output filtering <br>
* 4. a) <strong>Either</strong> invoke the next entity in the chain using
* the FilterChain object (<code>chain.doFilter()</code>), <br>
* 4. b) <strong>or</strong> not pass on the request/response pair to the
* next entity in the filter chain to block the request processing<br>
* 5. Directly set headers on the response after invocation of the next
* entity in the filter chain.
*
* @param request The request to process
* @param response The response associated with the request
* @param chain Provides access to the next filter in the chain for this
* filter to pass the request and response to for further
* processing
*
* @throws IOException if an I/O error occurs during this filter's
* processing of the request
* @throws ServletException if the processing fails for any other reason
*/
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException;
/**
* Called by the web container to indicate to a filter that it is being
* taken out of service. This method is only called once all threads within
* the filter's doFilter method have exited or after a timeout period has
* passed. After the web container calls this method, it will not call the
* doFilter method again on this instance of the filter. <br>
* <br>
*
* This method gives the filter an opportunity to clean up any resources
* that are being held (for example, memory, file handles, threads) and make
* sure that any persistent state is synchronized with the filter's current
* state in memory.
*
* The default implementation is a NO-OP.
*/
public default void destroy() {
}
}
- 스프링의 독자적인 기능이 아닌 자바 서블릿에서 제공하는 기능이다
- 스프링 프레임워크에서 필터로 인증 등 다양한 작업을 하는데 사용된다
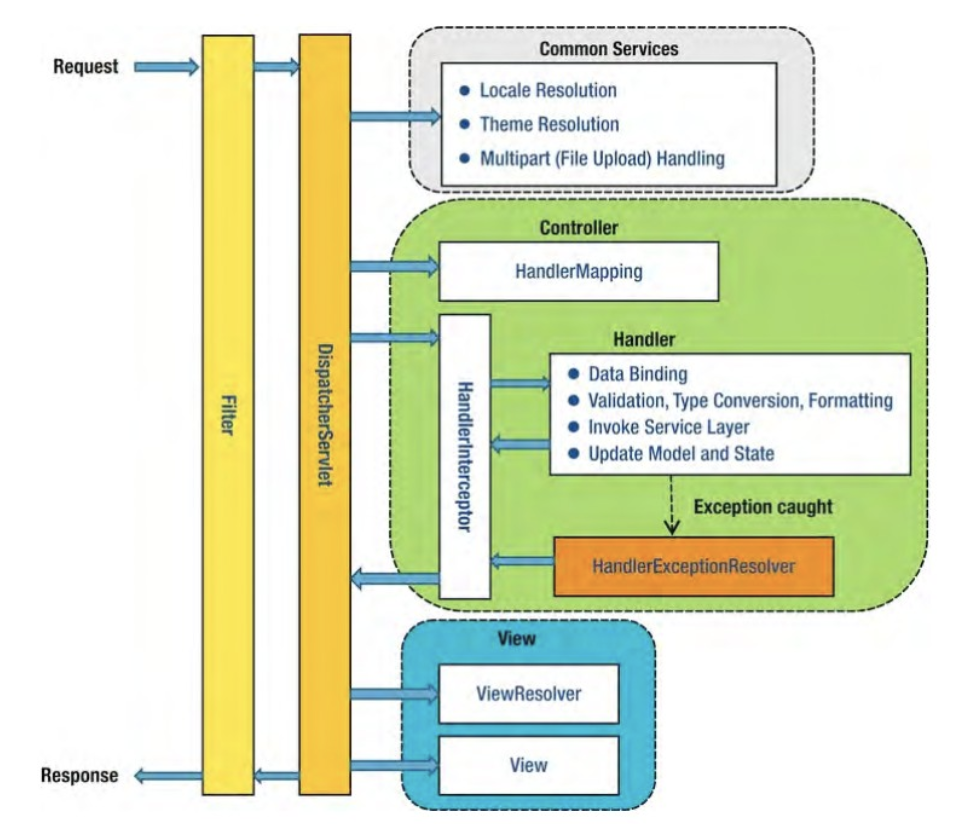
위 그림은 스프링 프레임워크에서 요청에 대한 라이프사이클을 나타낸 그림이다. 스프링 프레임워크로 들어온 요청이 DispatcherServlet에 의해 컨트롤러에 매필된다. 필터는 요청이 DispatcherServlet에 의해 다루어지기 전과 후에 동작한다.
flowchart LR
요청[요청] <--> 필터1[필터] <--> 필터2[필터] <--> 필터3[필터] <--> 자원[자원]
또한 Filter는 FilterChain을 통해 여러 필터가 연쇄적으로 동작하게 할 수 있다
Filter는 어디에 쓰일까
필터는 주로 요청에 대한 인증, 권한 체크 등을 하는데에 쓰인다
구체적으로 들어온 요청이 DispatcherServlet에 전달되기 전에 헤더를 검사해 인증 토큰이 있는지 없는지, 올바른지 올바르지 않은지 등을 검사할 수 있다.
Filter의 사용법
클래스를 만들어서 인터페이스를 구현해서 만들 수 있다
Filter는 메소드 세 가지를 가지고 있다
init(): 필터가 생성될 때 수행되는 메소드doFilter(): Request, Response가 필터를 거칠 때 수행되는 메소드destroy(): 필터가 소멸될 때 수행되는 메소드
위 세가지 메소드를 구현하면 필터가 된다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
public class SampleFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("SampleFilter Generated");
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("SampleFilter Start");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest, servletResponse);
log.info("SampleFilter Finish");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("SampleFilter destroy.");
}
}
위처럼 만들면 된다. 그리고 Filter가 여러 개 만들어질 수 있다고 했는데 이는 FilterRegistrationBean의 setOrder() 메소드로 결정할 수 있다
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
@Configuration
public class FilterConfig {
@Bean
public void runSomeFilterRegistration() {
someFilterRegistration();
}
private FilterRegistrationBean<SampleFilter> someFilterRegistration() {
FilterRegistrationBean<SomeFilter> registration = new FilterRegistrationBean<>();
registration.setFilter(new SampleFilter());
registration.addUrlPatterns("/sample/*"); // url 패턴 설정
registration.addInitParameter("param1", "param_value1"); // 파라미터 설정
registration.setName("sample-filter"); // 필터명 설정
registration.setOrder(1); // 순서 설정
return registration;
}
}
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.